Sodium hyaluronate is a salt form of hyaluronic acid (HA). HA is a large organic molecule produced by the body which serves many important functions. It can be used as a supplement for a wide range of health benefits.
” Sodium Hyaluronate (HA) provides a relatively safe alternative for patients for whom conventional therapy has failed” (NIH.gov)

What is Sodium Hyaluronate?
Sodium hyaluronate is a form of hyaluronic acid (HA). Essentially, a sodium hyaluronate molecule is an HA molecule with sodium atoms attached to it, which can be used easily by your body. Its name comes from the terms “hyaloid,” meaning vitreous or glass-like, and uronic acid, an organic sugar-based acid. A healthy sized adult has about 15 grams of HA in their body.1
Hyaluronic acid, also called hyaluronate or hyaluronan, is a type of glycosaminoglycan (GAG).1 GAGs are long chains made of multiple sugar molecules linked together. They are water soluble and elastic. Your body uses GAGs for structural support and as lubricants.


How Does Your Body Use Sodium Hyaluronate?
Sodium hyaluronate is produced by cells all throughout your body. It is particularly abundant in your nervous system, including your brain and spinal column, and in your connective tissues (e.g. skin, bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons). Cells secrete HA and other GAGs as a part of the extracellular matrix.1 This matrix is a network of proteins and other structural molecules that give strength to the tissues in your body and provide a scaffold for your cells to attach to. HA is also a part of the synovial fluid which cushions your joints and the vitreous fluid that fills your eyes.1

Is Sodium Hyaluronate Safe?
Sodium hyaluronate, along with other forms of HA, is very safe to use. It is a naturally-occurring substance that your body already produces in large quantities. Many clinical trials have been conducted on the safety and efficacy of HA for a number of different uses. In these, HA has not caused any major adverse effects on humans when taken orally as a supplement, applied topically, or injected.2, 3


Sodium Hyaluronate for Skin Health
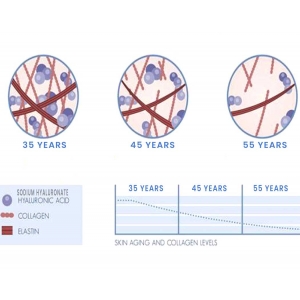
Half of all the HA in your body is located in your skin. Like collagen, HA helps keep your skin strong and flexible. It is also important for keeping your skin hydrated by holding moisture in. As an integral structural component, HA is important for wound-healing and rebuilding damaged skin.4
As you age, your skin cells start producing less and less HA. When this happens, your skin loses its integrity and becomes less taut and flexible.5 Supplementing with HA can help restore your skin and reduce signs of aging. Many cosmetic products, like creams and lotions, contain HA which can be applied topically.6 Some people also get injections of HA filler which can plump up skin and reduce wrinkles.7 HA scaffolds are also used to help skin heal faster.8


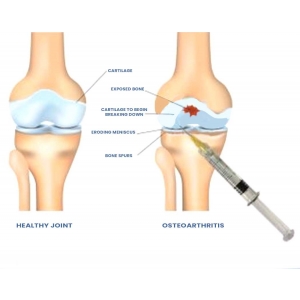
Sodium Hyaluronate for Joint Health
Sodium hyaluronate is abundant in the synovial fluid that cushions your joints. It fills in the space between two bones and allows them to move smoothly without rubbing against each other. When the components of this fluid become disrupted, inflammation and erosion can happen in the joint, contributing to arthritis.
Injecting HA into joints such as knees and hips can help replenish synovial fluid and reduce the symptoms of arthritis.9 Taking HA orally can help in mild cases of arthritis as well.10 Scientists are now also studying the use of HA scaffolds for getting cartilage to repair itself.11

Other Uses for Sodium Hyaluronate
Since sodium hyaluronate is used in so many parts of the body, researchers are finding more and more ways it can be used to improve our health. Here are a few of the recently discovered medical uses for HA:
- Reducing upper airway inflammation12
- Lower rate of urinary tract infections (UTIs)13
- Managing dry eye disease14
- Scaffolds for re-growing nerves or blood vessels15
- Carriers for drug delivery16
[1] A Fallacara, E Baldini, S Manfredini, and S Vertuani. 2018. "Hyaluronic Acid in the Third Millennium." Polymers. 10(7):701. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6403654/
[2] SL Matarasso, JD Carruthers, and ML Jewell. 2006. "Consensus recommendations for soft-tissue augmentation with nonanimal stabilized hyaluronic acid (Restylane)." Plast Reconstr Surg. 117(3 Suppl):3S-34S; discussion 35S-43S. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16531934
[3] RD Altman. 2003. "Status of hyaluronan supplementation therapy in osteoarthritis." Curr Rheumatol Rep. 5(1):7-14. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12590879
[4] WY Chen and G Abatangelo. 1999. "Functions of hyaluronan in wound repair." Wound Repair Regen. 7(2):79-89. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10231509
[5] E Papakonstantinou, M Roth, and G Karakiulakis. 2012. "Hyaluronic acid: A key molecule in skin aging." Dermato-endocrinology. 4(3):253-258. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/PMC3583886/
[6] M Essendoubi, C Gobinet, R Reynaud, JF Angiboust, M Manfait, and O Piot. 2016. "Human skin penetration of hyaluronic acid of different molecular weights as probed by Raman spectroscopy." Skin Res Technol. 22(1):55-62. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Jean-Francois_Angiboust/publication/275053701_Human_skin_penetration_of_hyaluronic_acid_of_different_molecular_weights_as_probed_by_Raman_spectroscopy/links/5a74361aa6fdcc53fe153706/Human-skin-penetration-of-hyaluronic-acid-of-different-molecular-weights-as-probed-by-Raman-spectroscopy.pdf
[7] K Walker and PM Zito. 2019. "Hyaluronic Acid," in StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing StatPearls Publishing LLC. Treasure Island (FL). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482440/
[8] MG Neuman, RM Nanau, L Oruna-Sanchez, and G Coto. 2015. "Hyaluronic acid and wound healing." J Pharm Pharm Sci. 18(1):53-60. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25877441
[9] E Maheu, RR Bannuru, G Herrero-Beaumont, F Allali, H Bard, and A Migliore. 2019. "Why we should definitely include intra-articular hyaluronic acid as a therapeutic option in the management of knee osteoarthritis: Results of an extensive critical literature review." Semin Arthritis Rheum. 48(4):563-572. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S004901721830235X?via%3Dihub
[10] M Ricci, GM Micheloni, M Berti, F Perusi, E Sambugaro, E Vecchini, and B Magnan. 2017. "Clinical comparison of oral administration and viscosupplementation of hyaluronic acid (HA) in early knee osteoarthritis." Musculoskelet Surg. 101(1):45-49.
[11] H Lin, AM Beck, K Shimomura, J Sohn, MR Fritch, Y Deng, EJ Kilroy, Y Tang, PG Alexander, and RS Tuan. 2019. "Optimization of photocrosslinked gelatin/hyaluronic acid hybrid scaffold for the repair of cartilage defect." J Tissue Eng Regen Med. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31066519
[12] L Pignataro, P Marchisio, T Ibba, and S Torretta. 2018. "Topically administered hyaluronic acid in the upper airway: A narrative review." International journal of immunopathology and pharmacology. 322058738418766739-2058738418766739. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5871036/
[13] JC Goddard and DAW Janssen. 2018. "Intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate for recurrent urinary tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis." Int Urogynecol J. 29(7):933-942. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6004275/
[14] AJ Mateo Orobia, J Saa, A Ollero Lorenzo, and JM Herreras. 2018. "Combination of hyaluronic acid, carmellose, and osmoprotectants for the treatment of dry eye disease." Clinical ophthalmology (Auckland, N.Z.). 12453-461. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5846763/
[15] S Wang, S Guan, Z Zhu, W Li, T Liu, and X Ma. 2017. "Hyaluronic acid doped-poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/chitosan/gelatin (PEDOT-HA/Cs/Gel) porous conductive scaffold for nerve regeneration." Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 71308-316. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27987712
[16] G Huang and H Huang. 2018. "Application of hyaluronic acid as carriers in drug delivery." Drug delivery. 25(1):766-772. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6058522/
-
Best Hyaluronic Acid - Benefits & Treatment
By Dr. KarenDecember 28, 2021 -
Hyaluronic Acid Foods
By Dr. AnnaAugust 14, 2022 -
Under Eye Wrinkles
By Dr. KarenDecember 17, 2021 -
Hyaluronic Acid and Vitamin C
By Dr. AnnaDecember 17, 2021 -
Hyaluronic Acid for Acne
By Dr. AnnaDecember 17, 2021



Search the blog
Article Categories
- All Articles (95)
- Rating Charts (1)
- Beauty & Skincare (17)
- FAQ (0)
- Hair Care (9)
- Health & Wellness (12)
- Anti-Aging (4)
- Kid's Health (0)
- Makeup (2)
- Men's Health (2)
- Oral Care (3)
- Sunscreen (7)
- Skin Tools & Treatments (10)
- Supplements (26)
- Videos (0)