The goal of a ketogenic diet is to induce your body into a state of ketosis. Once in this state, your body burns stored fat rapidly. There are a few ways to tell if you have entered ketosis, from signs and symptoms to commercial test kits.

What Happens in Your Body during Ketosis?
In a normal diet, much of your calories come in the form of carbohydrates. Once in your body, these carbs are broken down into glucose, a simple sugar molecule. Glucose is eventually converted into other metabolites and used to produce energy by your cells’ mitochondria.1
If you stop consuming carbs, your cells no longer have glucose as a source of energy. The metabolic pathways in your cells have to switch and start using a different calorie source. In this case, your body starts breaking fat reserves into fatty acids and ketone bodies, which circulate in your bloodstream and are taken up by cells throughout your body. There, these ketone bodies are processed into the same metabolites that your mitochondria use to produce energy.1

Keto Flu Symptoms
For the first three to seven days, your body is undergoing glucose withdrawal. High energy-consuming organs, especially your brain, are used to having glucose as a fast energy source, and have to undergo a transition to primarily fat use when you cut out the carbs. During this time, you may experience any of a number of common symptoms, including:2,3
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Irritability
- Poor concentration
- Difficulty focusing (brain fog)
- Low motivation
- Dizziness
- Sugar cravings
- Nausea
- Muscle cramps
- Vomiting
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Muscle weakness
- Stomachaches
- Difficulty sleeping
Experiencing symptoms of keto flu is a good indicator that your body has entered ketosis. However, you will need to use other means to tell if you are staying in ketosis for longer or not.

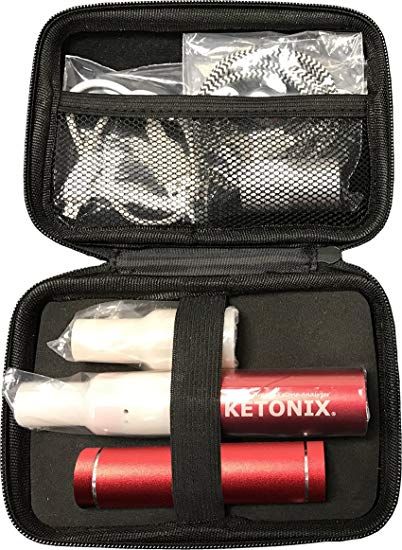
Breath Acetone
A byproduct of fat metabolism is acetone - the same chemical that is in fingernail polish remover. On a very low-carb diet, when your cells are predominantly utilizing fats for energy production, the concentration of acetone rises in your blood and, subsequently, your breath. Bad-smelling breath is a common complaint of people on the keto diet, but also a good indicator that it is working.
Recently, breath acetone meters have been developed which can measure the level of fat metabolism in the body. Compared to blood and urine tests, breath acetone testing is even more reliable and less influenced by other metabolic factors.4 Since they rely on specialized sensors, breath acetone meters are more expensive than other tests, but they are reusable and easy to take anywhere.

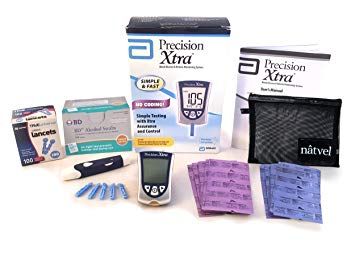
Blood Ketones
Blood tests have historically been the most accurate means of measuring your blood ketone levels. This can be done using a finger prick and a home test kit. Though fast and reliable, the finger prick can be uncomfortable. It also requires a reusable device and disposable strips which can end up being a bit expensive altogether. Many devices also measure blood glucose.
Ketosis is defined as a blood concentration of ketone bodies of 0.5-3.0 mm/L.5 Lower than this range means you need to cut your carb intake more to achieve true ketosis. If you have a ketone concentration higher than 3.0 mm/L, however, you should see your doctor.

Urine Ketones
For cheaper, less-invasive ketosis monitoring than blood testing, urine test strips are inexpensive and easy to use. However, the ketone level detected in urine can be influenced by other factors, such as fluid dynamics and the presence of other metabolites. Urine ketone tests are less reliable than blood ketone tests, but they nonetheless can give you a good indication of how your diet is going.6
[1] Gano LB, Patel M, Rho JM. 2014. “Ketogenic diets, mitochondria, and neurological diseases.” J Lipid Res. Nov; 55(11):2211-2228. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24847102
[2] Mayo Clinic. March 8, 2018. “The truth behind the most popular diet trends of the moment.” Healthy Lifestyle: Weight Loss. https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/weight-loss/in-depth/the-truth-behind-the-most-popular-diet-trends-of-the-moment/art-20390062
[3] Mayo Clinic. August 29, 2017. “Low-carb diet: Can it help you lose weight?” Healthy Lifestyle: Weight Loss. https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/weight-loss/in-depth/low-carb-diet/art-20045831
[4] Günther AT, Kompalla JF, Landis H, Theodore SJ, Geidl B, Sievi NA, Kohler M, Pratsinis SE, Gerber PA. 2018. “Guiding Ketogenic Diet with Breath Acetone Sensors.” Sensors (Basel). Oct 28; 18(11):E3655. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6264102/
[5] López Siguero JP, Moreno Molina JA, Borrás Pérez MV, Pinzón Martín JL, Brea Molina JI, del Pino de la Fuente A, Parramón Pons M. 2007. “[Blood glucose and ketone monitoring in type 1 diabetic patients in the controlled environment of a summer camp.]” An Pediatr (Barc). Apr; 66(4):387-392. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17430716
[6] Kuru B, Sever M, Aksay E, Dogan T, Yalcin N, Eren ES, Ustuner F. 2016. “Comparing Finger-stick β-Hydroxybutyrate with Dipstick Urine Tests in the Detection of Ketone Bodies.” Turk J Emerg Med. Feb 26; 14(2):47-52. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27331169
-
Keto Electrolytes
By Dr. KarenDecember 20, 2021 -
Supplements for Ketogenic Diet
By Dr. KarenAugust 14, 2022 -
Keto Diet for Beginners
By Dr. AnnaAugust 14, 2022 -
Keto Diet Food List
By Dr. AnnaAugust 14, 2022 -
How Long Does it Take to Get Into Ketosis
By Dr. KarenDecember 21, 2021 -
Vegetarian Keto
By Dr. KarenAugust 14, 2022

Search the blog
Article Categories
- All Articles (95)
- Rating Charts (1)
- Beauty & Skincare (17)
- FAQ (0)
- Hair Care (9)
- Health & Wellness (12)
- Anti-Aging (4)
- Kid's Health (0)
- Makeup (2)
- Men's Health (2)
- Oral Care (3)
- Sunscreen (7)
- Skin Tools & Treatments (10)
- Supplements (26)
- Videos (0)