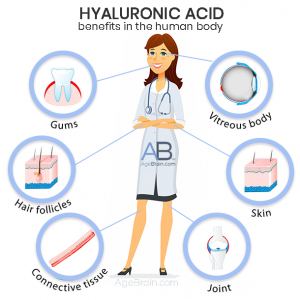
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a naturally occurring molecule that your body uses for many functions. Taking HA as a supplement can reduce signs of aging and help your body heal itself. You can also obtain HA from certain foods in which it is abundant.

”HA is widely distributed as a medicine, cosmetic, food, and, recently marketed in Japan as a popular dietary supplement to promote skin moisture” (NIH.gov)

Hyaluronic acid, also called hyaluronan or hyaluronate, is a type of glycosaminoglycan (GAG).1 Like other GAGs, HA consists of long chains made of multiple sugar molecules that are linked together. It is water-soluble and elastic, so your body uses it for structural support and as a lubricant.
HA is produced by cells all throughout your body. It is particularly abundant in your nervous system, including your brain and spinal column, and in your connective tissues (e.g. skin, bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons). Cells secrete HA and other GAGs as a part of the extracellular matrix.1 This matrix is a network of proteins and other structural molecules that give strength to the tissues in your body and provide a scaffold for your cells to attach to.

Benefits of Supplementing with Hyaluronic Acid
Hyaluronic acid is available as a nutritional supplement in the United States, Europe, and other countries. Multiple clinical trials have shown that HA is safe when taken orally. Some evidence exists that it can survive digestion in the stomach and can be absorbed intact into the bloodstream.1
One of the most common uses for HA supplementation is skin health and healthy aging. Your skin loses its ability to produce HA over time, which contributes to wrinkles and skin that sags. Supplementing with HA can improve the integrity of your skin and reduce the appearance of aging.2
HA is now also used as an alternative or complimentary option for managing arthritis. Naturally, it is a major component of the synovial fluid that cushions your joints. Taking extra HA can reduce inflammation in arthritic joints and help cartilage repair itself.3-5
There are a number of other possible uses for HA supplements that are now being investigated. Some evidence suggests that it can help with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and other digestive disorders.6 It can also reduce the incidence of urinary tract infections (UTIs).7

Bone Broth has a Very High Hyaluronic Acid Content
Bone broth has become a dietary trend recently, although it has been an important nutritional source for humans since our primitive years. By stewing bone and gristle for a long time, the tough matrix breaks down and releases proteins, minerals, and other nutrients into the liquid. The resulting broth is rich in skeletal nutrients like collagen, calcium, and HA.8, 9
To make bone broth, place bones of any type into a pot, cover with water, and simmer for a minimum of 24 hours. You can add herbs and other flavorings to your desire. Bones can be obtained from a butcher, or you can save your own from other meals.

Meats are Good Sources of Hyaluronic Acid
Hyaluronic acid is an important component of strong protein networks. Protein-rich foods, therefore, have a high content of HA. Meats, especially red meats, are good sources of HA. You can also get decent amounts of HA from white meats, seafood, and eggs. It is now being used as an additive to some meat products, though eating processed meats like hot dogs and lunch meats should be kept to a minimum to avoid their negative health effects.
Hyaluronic acid is an important component of strong protein networks. Protein-rich foods, therefore, have a high content of HA. Meats, especially red meats, are good sources of HA. You can also get decent amounts of HA from white meats, seafood, and eggs. It is now being used as an additive to some meat products, though eating processed meats like hot dogs and lunch meats should be kept to a minimum to avoid their negative health effects.


Plant Sources of Hyaluronic Acid
Vegans and vegetarians need not despair, for there are plant-based foods available with high HA content. Others, such as vegetables rich in magnesium, stimulate your body to produce more HA itself.10-12 Some good options include:
- Citrus fruits and citrus peel
- Root vegetables
- Soybeans and soy products
- Cole crops (cabbage, kale, broccoli, brussels sprouts, etc.)
- Olives
- Green leaf vegetables (spinach, lettuce, etc.)
Vegans and vegetarians need not despair, for there are plant-based foods available with high HA content. Others, such as vegetables rich in magnesium, stimulate your body to produce more HA itself.10-12 Some good options include:
- Citrus fruits and citrus peel
- Root vegetables
- Soybeans and soy products
- Cole crops (cabbage, kale, broccoli, brussels sprouts, etc.)
- Olives
- Green leaf vegetables (spinach, lettuce, etc.)

Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a naturally occurring molecule that your body uses for many functions. Taking hyaluronic acid daily can help ease joint pain, reduce signs of aging and help your body heal itself. You can obtain hyaluronic acid from certain foods in which it is abundant or by taking a hyaluronic acid supplement.
Studies have found that taking a hyaluronic acid supplement high in purity is effective in helping with joint discomfort. One study saw improvement specifically with decreasing pain and improving physical function with knee osteoarthritis by taking 80mg of hyaluronic acid daily. [11]
Research has shown that the eyes and joints (cartilaginous tissues) of animals contain the highest concentration of hyaluronic acid (HA). Fish bodies and heads (specifically mackerel, sea bream & eels) also have high amounts of hyaluronic acid. [12]
Studies have shown Hyaluronic Acid (HA) is safe to take daily in high doses. Hyaluronic Acid is naturally produced by the body and rarely has negative side effects or allergic reactions. One study tested taking 200mg of hyaluronic acid supplement daily for a year with no harmful side effects. [13]
[1] A Fallacara, E Baldini, S Manfredini, and S Vertuani. 2018. "Hyaluronic Acid in the Third Millennium." Polymers. 10(7):701. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6403654/
[2] E Papakonstantinou, M Roth, and G Karakiulakis. 2012. "Hyaluronic acid: A key molecule in skin aging." Dermato-endocrinology. 4(3):253-258. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/PMC3583886/
[3] RD Altman. 2003. "Status of hyaluronan supplementation therapy in osteoarthritis." Curr Rheumatol Rep. 5(1):7-14. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12590879
[4] TL Huang, CH Yang, G Yanai, JY Liao, S Sumi, and KC Yang. 2018. "Synergistic effect of l-ascorbic acid and hyaluronic acid on the expressions of matrix metalloproteinase-3 and -9 in human chondrocytes." J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 106(5):1809-1817. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28914997
[5] E Maheu, RR Bannuru, G Herrero-Beaumont, F Allali, H Bard, and A Migliore. 2019. "Why we should definitely include intra-articular hyaluronic acid as a therapeutic option in the management of knee osteoarthritis: Results of an extensive critical literature review." Semin Arthritis Rheum. 48(4):563-572. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S004901721830235X?via%3Dihub
[6] B Palmieri, A Merighi, D Corbascio, V Rottigni, G Fistetto, and A Esposito. 2013. "Fixed combination of hyaluronic acid and chondroitin-sulphate oral formulation in a randomized double blind, placebo controlled study for the treatment of symptoms in patients with non-erosive gastroesophageal reflux." Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 17(24):3272-8. https://www.europeanreview.org/article/6160
[7] JC Goddard and DAW Janssen. 2018. "Intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate for recurrent urinary tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis." Int Urogynecol J. 29(7):933-942. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6004275/
[8] JL Hawkins and PL Durham. 2018. "Enriched Chicken Bone Broth as a Dietary Supplement Reduces Nociception and Sensitization Associated with Prolonged Jaw Opening." J Oral Facial Pain Headache. 32(2):208-215. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Paul_Durham/publication/323596226_Enriched_Chicken_Bone_Broth_as_a_Dietary_Supplement_Reduces_Nociception_and_Sensitization_Associated_with_Prolonged_Jaw_Opening/links/5c6839444585156b5701495f/Enriched-Chicken-Bone-Broth-as-a-Dietary-Supplement-Reduces-Nociception-and-Sensitization-Associated-with-Prolonged-Jaw-Opening.pdf
[9] C Saint-Germain. 1997. "The Production of Bone Broth: A Study in Nutritional Exploitation." Anthropozoologica. 25-26153-156. http://sciencepress.mnhn.fr/sites/default/files/articles/pdf/az1998n25-26a18.pdf
[10] C Kim, J Ji, S Ho Baek, JH Lee, IJ Ha, SS Lim, HJ Yoon, Y Je Nam, and KS Ahn. 2019. "Fermented dried Citrus unshiu peel extracts exert anti-inflammatory activities in LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophages and improve skin moisturizing efficacy in immortalized human HaCaT keratinocytes." Pharmaceutical biology. 57(1):392-402.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6566750/
[11] Kalman, D.S., Heimer, M., Valdeon, A. et al. Effect of a natural extract of chicken combs with a high content of hyaluronic acid (Hyal-Joint®) on pain relief and quality of life in subjects with knee osteoarthritis: a pilot randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Nutr J 7, 3 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-7-3
[12] Shoichiro Ozaki. Food Containing Hyaluronic Acid and Chondroitin is Essential for Anti-Aging. Int J Aging Clin Res 2016, 1: 101. https://agebrain.com/references/article-IJACR-101.pdf